Year 6 Physical Science
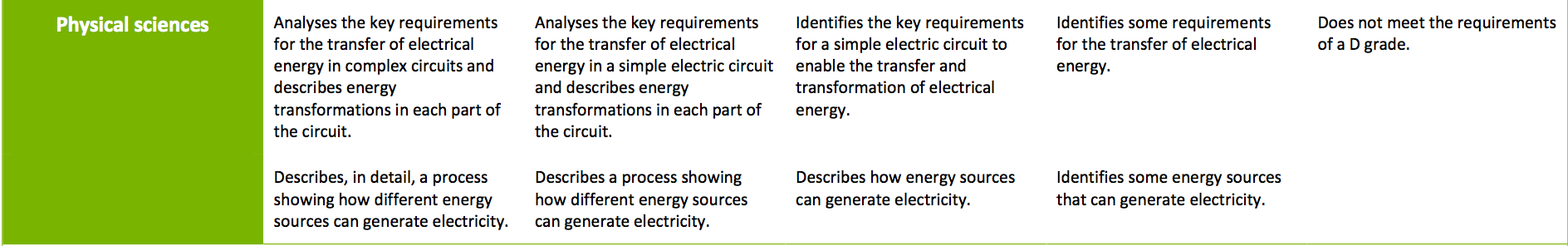
Electrical energy can be transferred and transformed in electrical circuits and can be generated from a range of sources (ACSSU097)
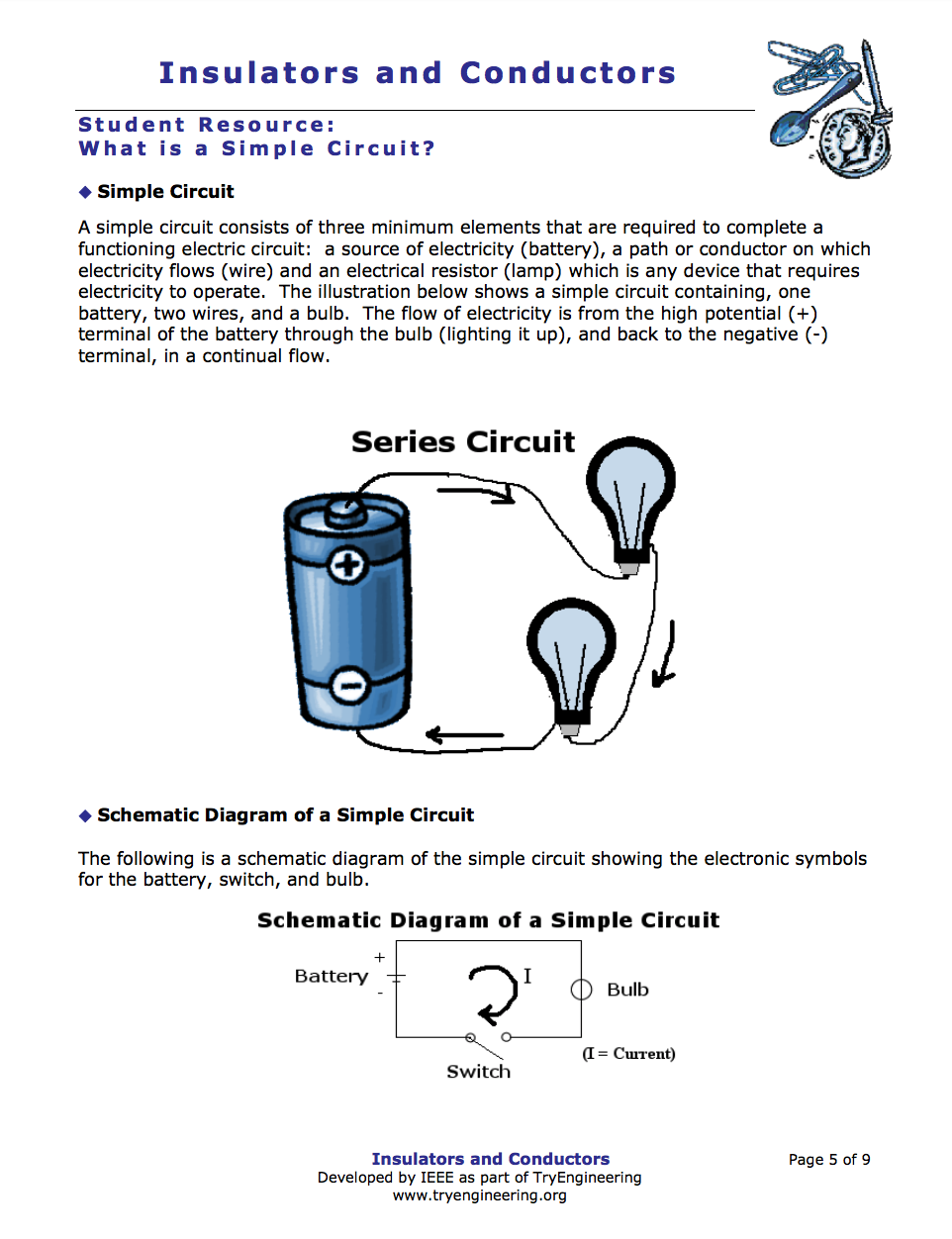
- recognising the need for a complete circuit to allow the flow of electricity
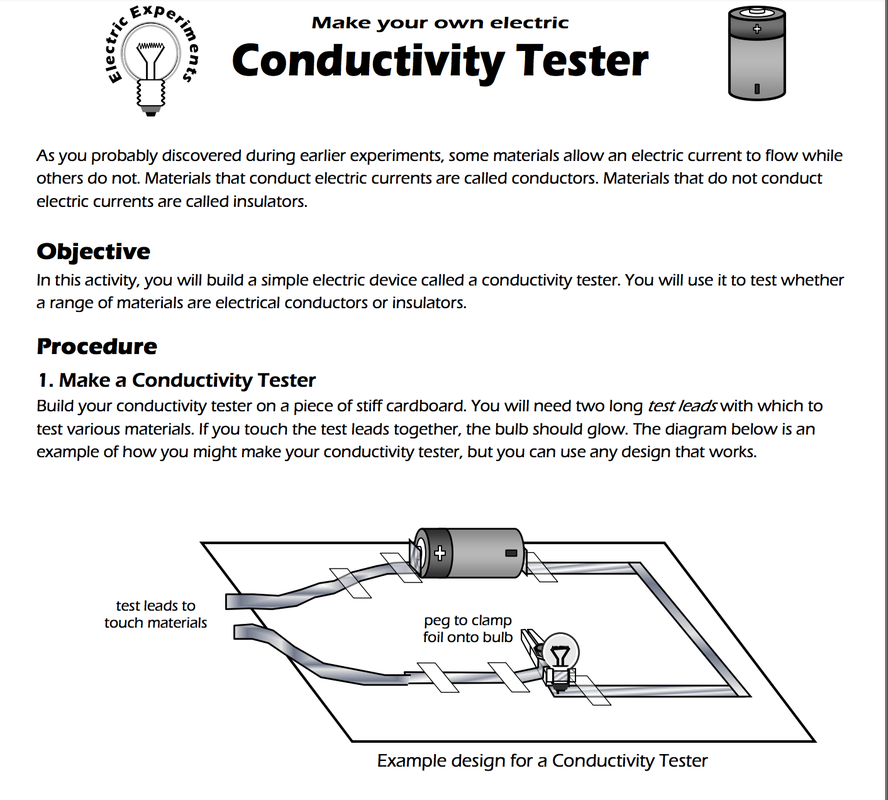
- investigating different electrical conductors and insulators
- exploring the features of electrical devices such as switches and light globes
- investigating how moving air and water can turn turbines to generate electricity
- investigating the use of solar panels
- considering whether an energy source is sustainable
Self directed Webquest
1. Electrical Safety
Watch the video below. Make a list of the electrical hazards that are mentioned.
2. ENERGY CHAINS
3. CURRENTS AND VOLTAGE
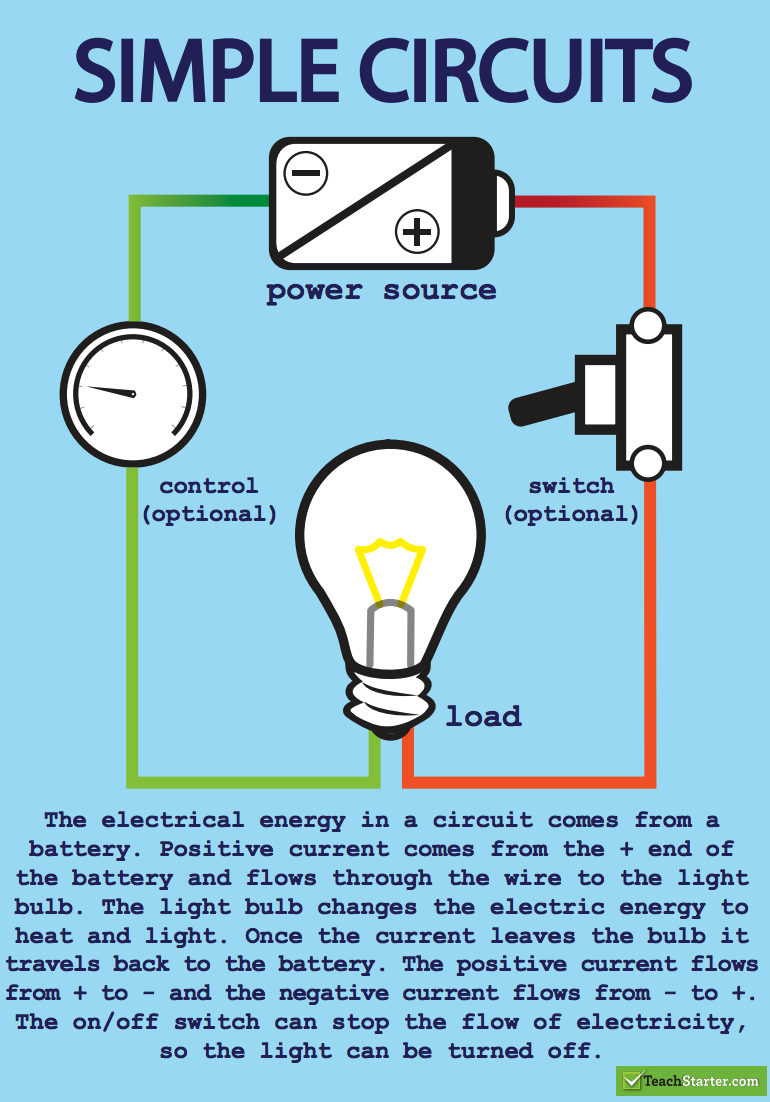
4. ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
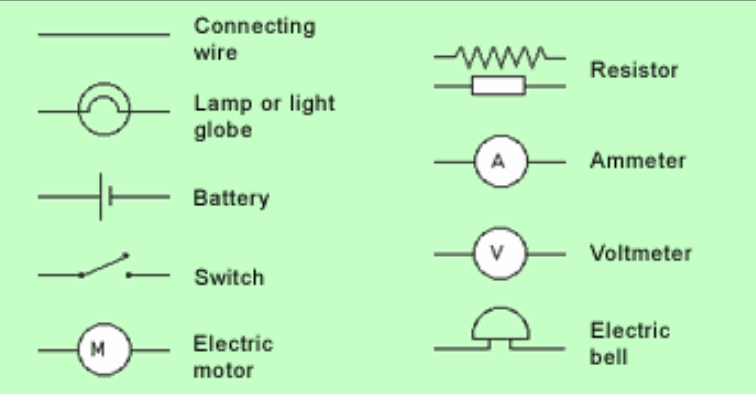
Electric circuits can be series or parallel. You need to know the symbols we use to draw circuit diagrams.
An ammeter measures electric current, in amps, by measuring how much charge is flowing in the circuit. A voltmeter measures, in volts, the difference in electrical energy between two points of a circuit.
An ammeter measures electric current, in amps, by measuring how much charge is flowing in the circuit. A voltmeter measures, in volts, the difference in electrical energy between two points of a circuit.
| insandcond.pdf | |
| File Size: | 164 kb |
| File Type: | |
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
STATIC ELECTRICITY
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Static Electricity
Take notes.
What is an atom?
What are atoms made up of?
What is Static Electricity? How does it occur?
What is an atom?
What are atoms made up of?
What is Static Electricity? How does it occur?